- Product Details
Keywords
Quick Details
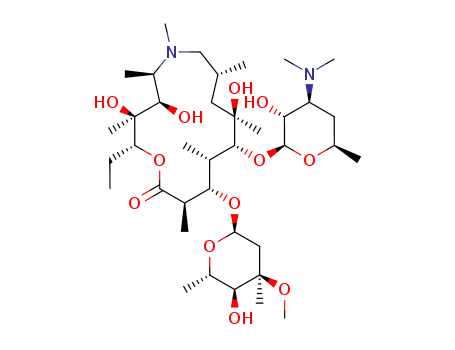
- ProName: Azithromycin
- CasNo: 83905-01-5
- Molecular Formula: C38H72N2O12
- Appearance: White or almost white crystalline powd...
- Application: Azithromycin is an antibiotic used to ...
- DeliveryTime: In one week or two weeks after the cot...
- PackAge: Inside: vacauumed aseptic PE bags, 25k...
- Port: sany port of china
- ProductionCapacity: 50 Metric Ton/Month
- Purity: 100%
- Storage: The product should be contained in uno...
- Transportation: as your requirement
- LimitNum: 25 Kilogram
Superiority
Specification ProductName …
Details
| Product Name | Azithromycin |
| CAS NO. | 83905-01-5 |
| Formual | C38H72N2O12 |
| Standard | FCC/USP/BP/EP |
| Molecular weight | 749.00 |
| Packing | Inside: vacauumed aseptic PE bags, 25kg per bag. Outside: carton or drum Packages size can also be offered according to customer requirement |
| Identification | The IR spectrum obtained with the substance to be examined should conform with that obtained with amoxicillin trihydrate CRS |
| Appearance | White or almost white crystalline powder |
| Identification | (1) IR: Conforms to the Azithromycin RS spectrum (2) HPLC: The retention time of azithromycin peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation, as obtained in the Assay |
| Specific rotation | -45°~-49°(Anhydrous subatance 20mg/ml dehydrated alcohol) |
| PH | 9.0~11.0(2mg/ml methanol-water(1:1)) |
| Water | 4.0~5.0% |
| Residue on ignition | ≤0.3% |
| Heavy metals | ≤25% |
| Assay | 945~1030μg/mg (C38H72N2O12)Based on anhydrous substance |
| Stability and storage | The product should be contained in unopened original package, protected from light in a dry place at low temperature ( ≤15℃ ). Once it is opened, please use it up in a short time. |
| Uses | Azithromycin is an antibiotic used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections, such as respiratory tract infections, sexually transmitted diseases and skin infections. This antibiotic only treats bacterial infections. It will not work for viral infections (e.g., common cold, flu). Unnecessary use or overuse of any antibiotic can lead to its decreased effectiveness. |